Would we enjoy the human touch of voice assistants when they are not real?
The growing technology behind artificial intelligence and machine learning will completely change the way we interact and connect with Contact Centers. We may have voice assistants calls on our behalf for inquiries and appointments, or we can make these phone calls ourselves to gain experience handling questions, searches, or certain tasks.
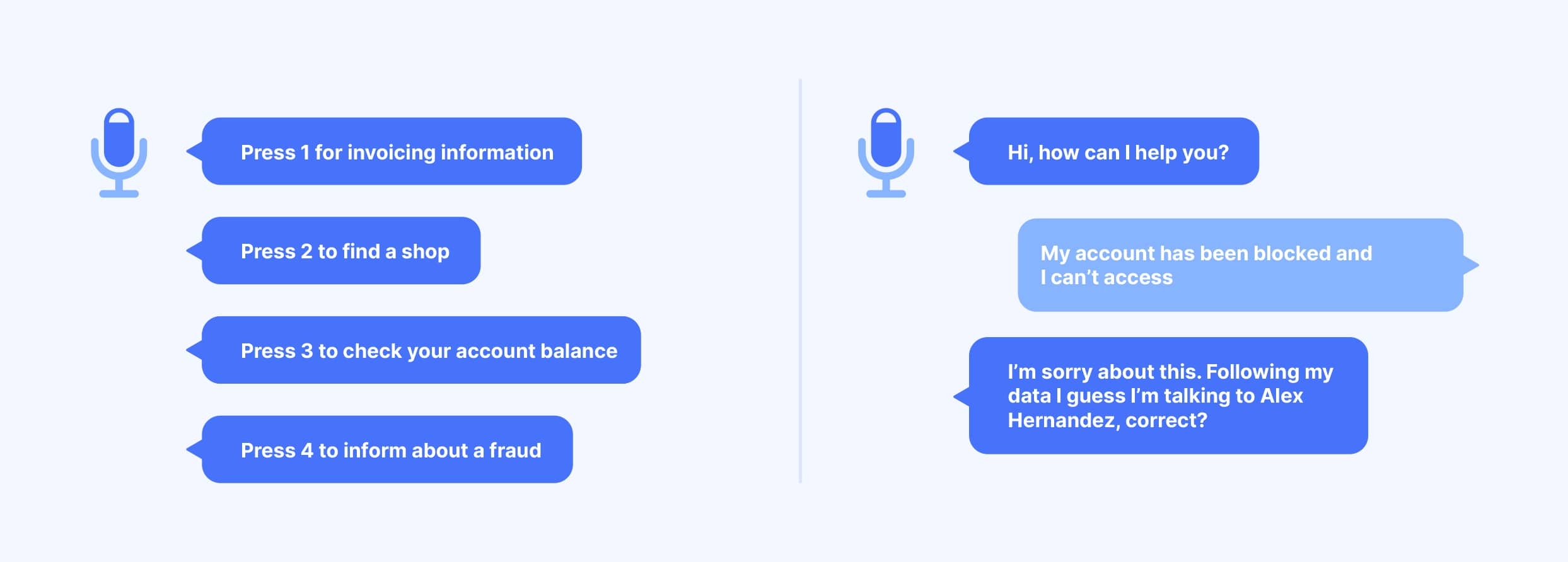
If we go one step further, how would the future of a Contact Center integrating artificial intelligence look? Instead of using bot messages to direct customers to a navigation, through a service system, in order to get a response, could the call experience become completely natural and conversational?
The technology that enables voice assistants is aimed at carrying out natural conversations and giving support and solving problems through phone calls. And this is a great opportunity to train AI to understand the full context of that query.
Let’s learn more about the viability of it in a typical customer phone call:
Personalized attention to the opening of the call
The first few seconds are used to set the tone for a phone call. Customers receive branded greetings to establish a quick trust by voice. There are assistants that offer multiple voices. The possibility of fully customizing the voices in call openings will be developed more and more, being able to initiate a conversation even with a favorite character or a brand spokesperson him or herself.
Easy identification
Before going deeply into the details of customers’ inquiries, they are often asked to provide personal information to verify their identity. With the help of voice assistants this process is simplified. Voice assistants act faster by recognizing numbers, names or addresses, or any other confidential information from customers’ profiles, avoiding the need of line transfers. This eliminates having to repeat this customer identity verification from line to line.
No transfers, less abandonment
Eliminating line transfers can really make a big difference. The abandonment rate for a call is closely related to the time a customer waits for assistance. Being on hold is a passive experience, and we all experience hanging up calls after waiting too long. Currently, the average acceptable rate is 5%, indicating that below 5% is considered a good customer service, while above 5% is considered problematic. But be careful, 5% in a competitive retail sector could be very high, and in a technology sector it could be correct.
This is the formula used to calculate the call abandon rate:
If customers don’t have to wait for transfers, repeat their identification, and the same agent are with them from the beginning of the call to the end, the abandon rate will be significantly lower.
The data to calculate your abandonment rate will be stored in the call abandonment reports within the ACD system, which must be integrated with your IVR.
Using an IVR we can configure the limit we want to set the time for the considered “short abandoned calls”. For example, those calls that are less than 5 seconds in queue can be qualified in another way, than not abandoned.
Understanding the customers
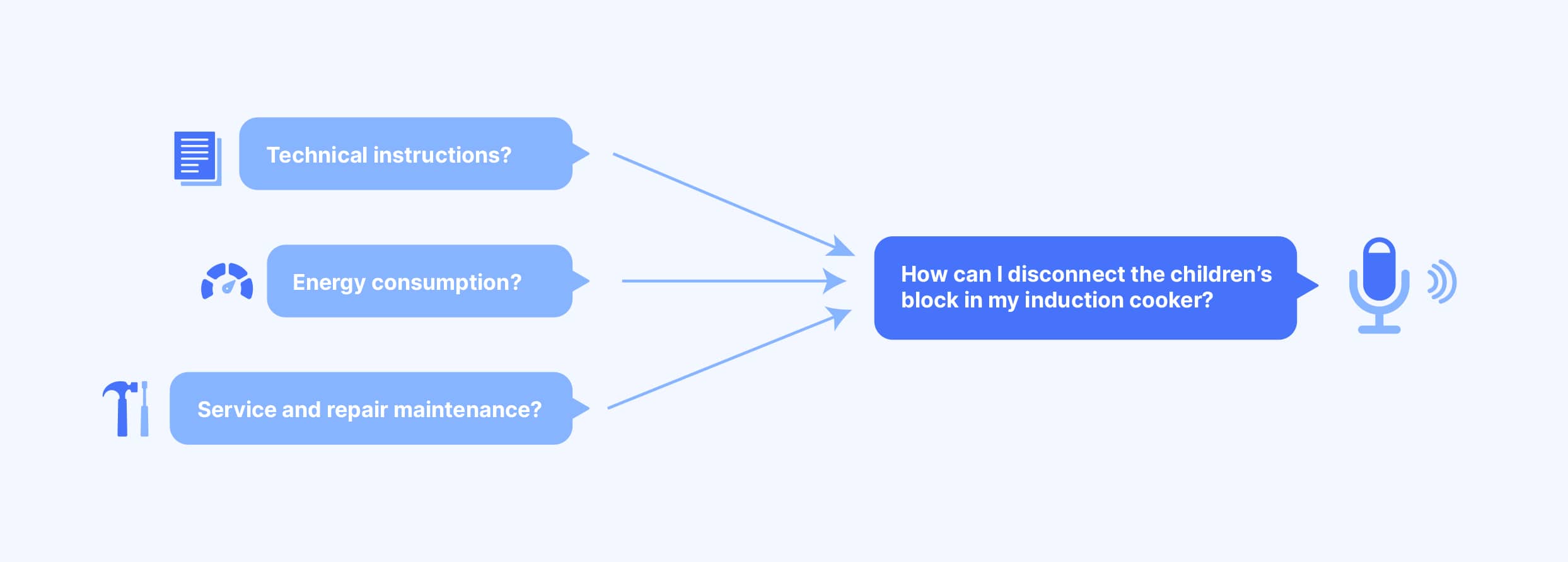
A critical part of voice assistant intelligence is accurately understanding our customers’ inquiries. A key challenge for voice assistants is understanding the entire context of the conversation, not just a sentence or two. In many cases, when we ask a question, we expect not only an answer, but also a set of sub-answers that contextualize our curiosity about a particular question.
The challenge for voice assistants is to fully understand the user and to do a correct follow up with the right questions to clarify the customer’s intention.
Some limitations
Great phone agents are excellent listeners. They do not interrupt customers when they speak and rely on a fluid conversation for customers to explain their intention before offering a solution. Also, voice assistants are being improved to respond naturally to copy people’s reactions. But understanding language is only one aspect of building conversations.
Understanding the context of a conversation and generating natural language responses have to do with situations in which people do not follow the “script”, which is something that is still a long way off, and there is still a lot to develop to get conversations well contextualized in an automatic way.
Conclusions
According to Statista, by 2023 the number of digital voice assistants will reach around 8 billion, a number that exceeds the world’s population. These numbers suggest that people will access information, make payments, and communicate with organizations through voice user interfaces from multiple environments. The accelerated adoption of voice assistants and the increasing convenience that means for people to interact with them are compelling reasons for brands and contact centers to use voice artificial intelligence to improve their customer experience and increase their revenue.
A voice assistant in contact centers alleviates the friction and frustration of callers’ daily requests and helps businesses avoid delayed response times during the periods of high call volumes.
With today’s AI, the virtual assistant answers your customers’ questions directly on the front end and provides your agents with the information and resources they need on the back end. The path to real-time self-service and artificial intelligence assistance in customer service provides enormous opportunities for forward-thinking companies.